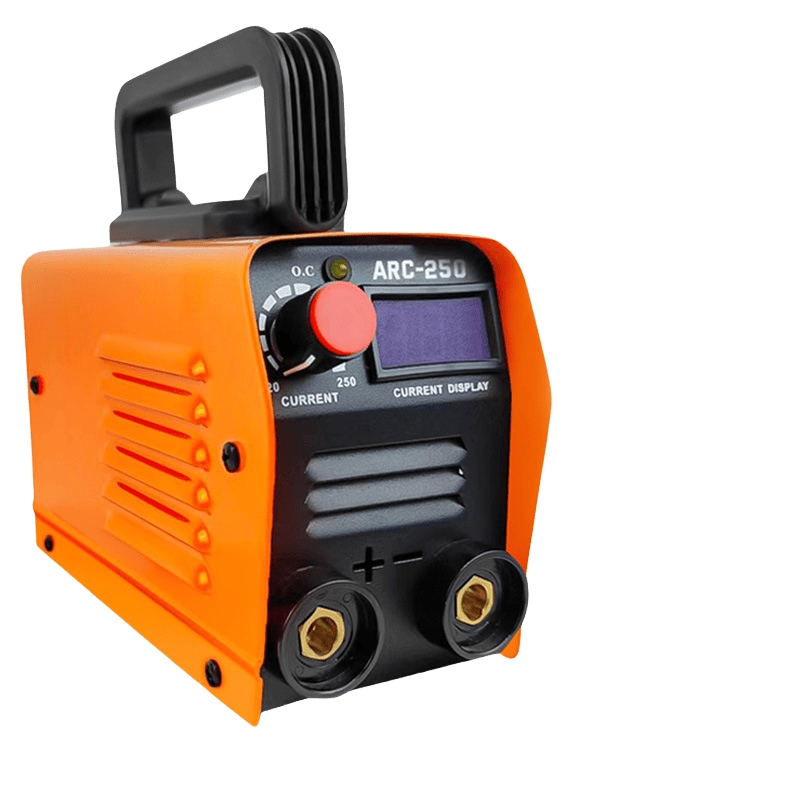
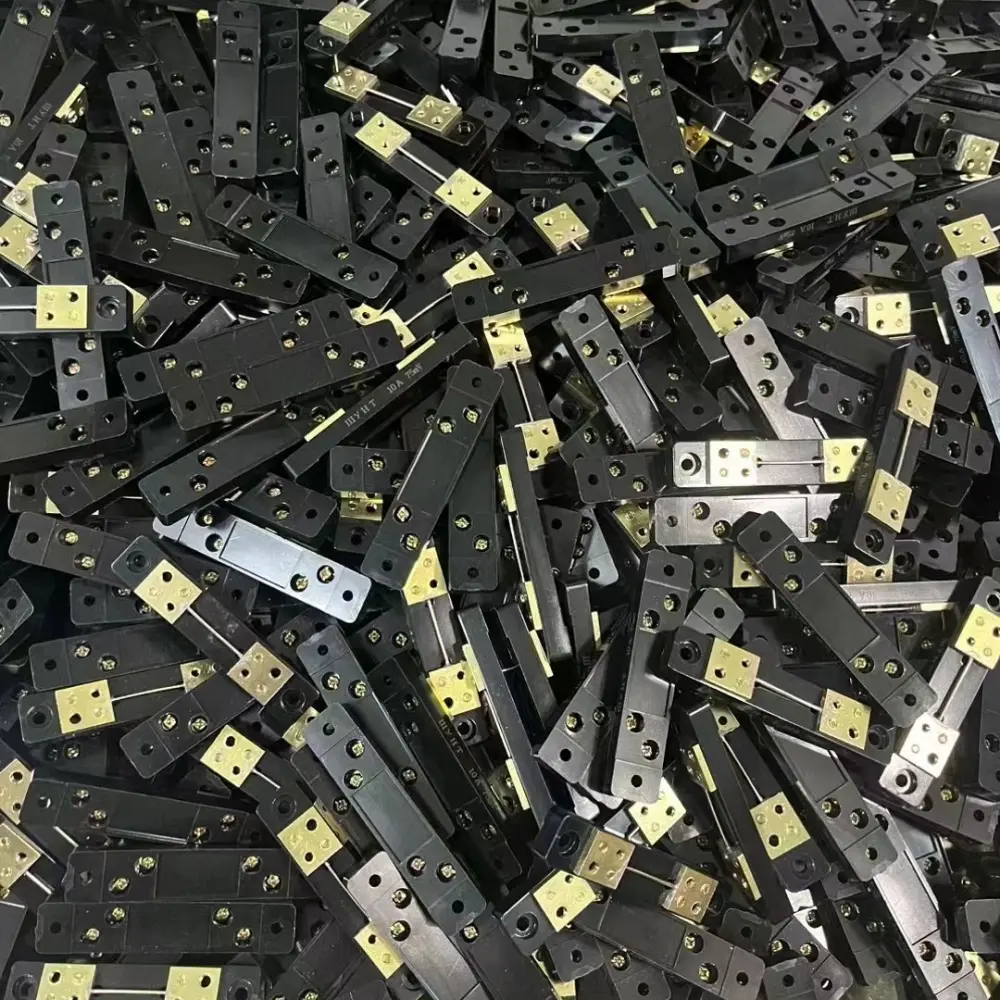
Are you struggling with current measurement in your electrical systems? DC current shunts are the solution you need. Let’s dive into their key features and applications.
DC current shunts are precise tools used for measuring current by creating a small, measurable voltage drop. They are used in various applications such as battery chargers, heaters, and plating baths.

DC current shunts are widely used to measure current in electrical systems, especially where precise measurements are crucial. From powering electric devices to ensuring the performance of battery management systems, shunts provide an efficient solution. In this article, we’ll take a closer look at what DC current shunts are, their construction, installation guidelines, and how to ensure long-term efficiency.
DC Current Shunts – Overview?
Have you ever wondered how current is measured in complex electrical systems? DC current shunts play a significant role in providing precise readings.
DC current shunts are precision resistors designed to measure high currents by generating a proportional voltage drop across them.
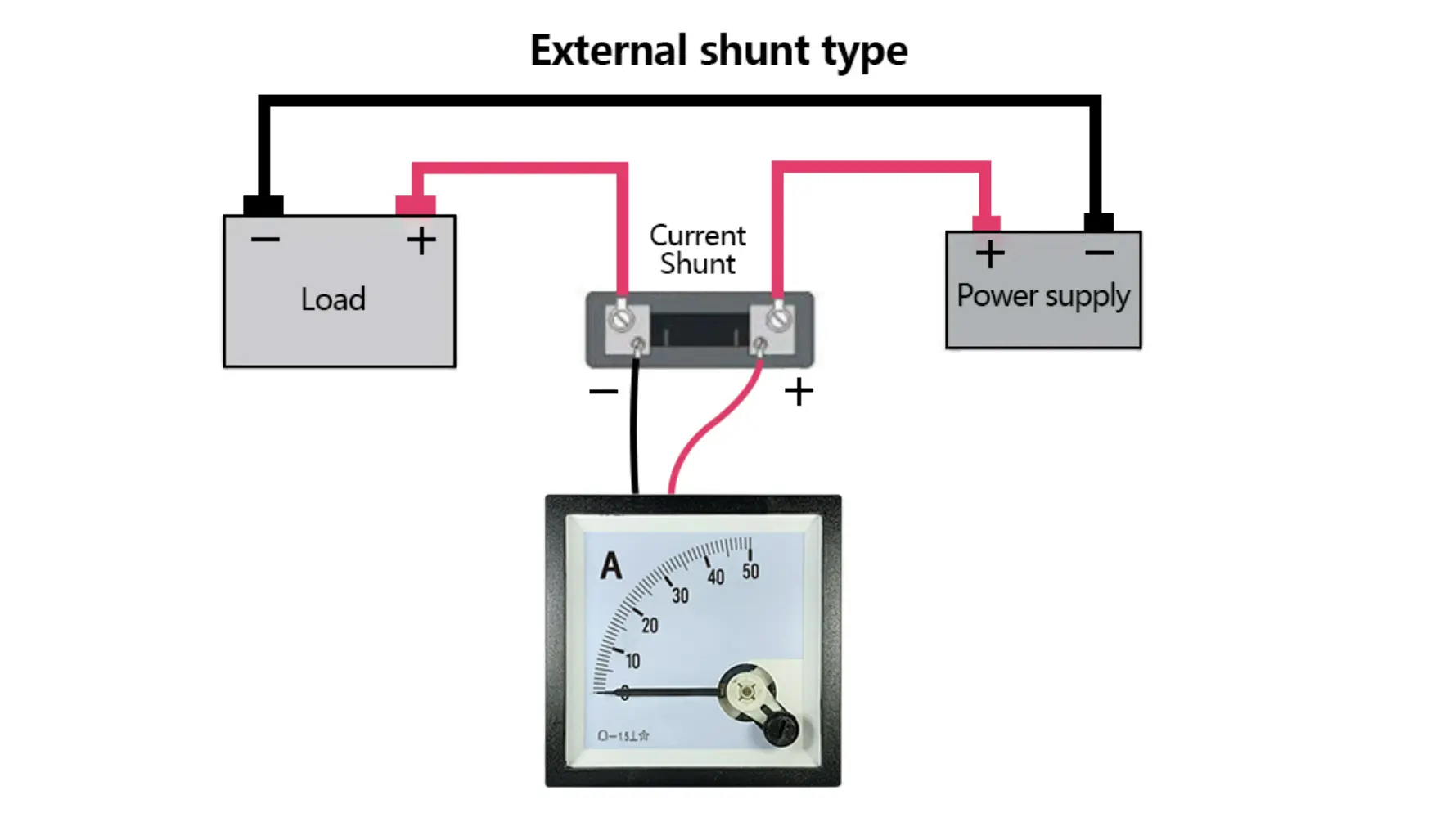
Common Applications of DC Current Shunts
DC current shunts are versatile and essential in various applications, where precision in current measurement is necessary. Some of the most common applications include:
- Battery Chargers: DC current shunts help monitor the current flowing into batteries, ensuring they are charged safely and efficiently.
- Heaters: Shunts are used in heater circuits to monitor the current and ensure optimal power usage.
- Plating Baths: In electroplating, accurate current measurement is essential for controlling the plating process, and shunts help monitor the current.
These applications show the critical role DC current shunts play in both industrial and consumer electronics, providing reliable and accurate measurements.
Construction & Material?
Curious about how DC current shunts are built and what materials they are made from? Let’s break it down.
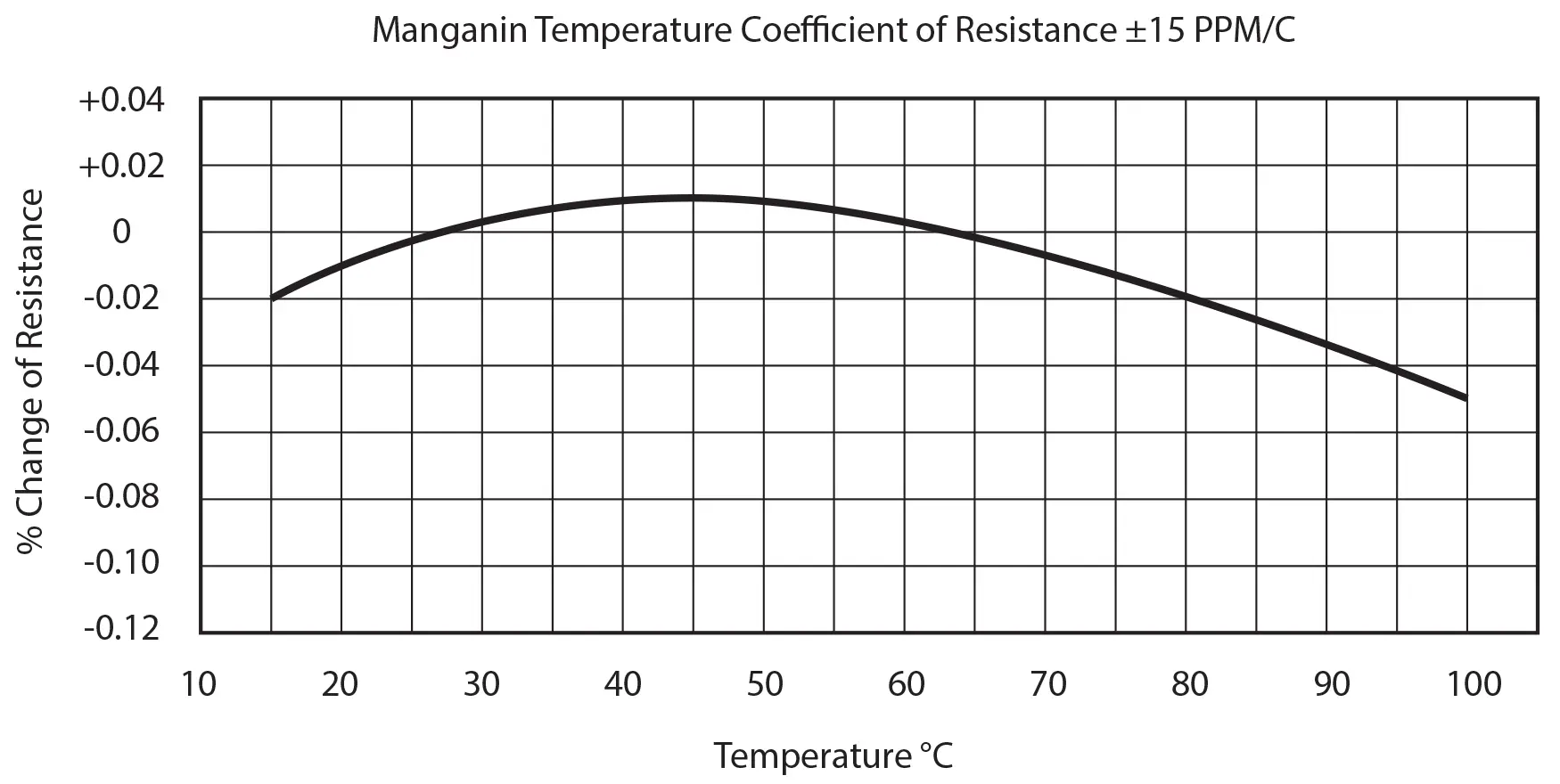
DC current shunts are typically made from manganin alloy, which offers low resistance and high stability under varying temperatures.

Material Composition
DC current shunts are primarily made of Manganin alloy, which consists of:
- Copper: 84%
- Manganese: 12%
- Nickel: 4%
This composition offers several benefits, such as low temperature coefficients, making manganin a stable material for high-precision current measurement.
Resistance Stability
A key feature of manganin alloy is its low temperature coefficient of about 0.0015%/°C, which ensures minimal resistance change even under fluctuating temperatures. This is crucial for maintaining consistent and accurate current readings, especially in environments with varying temperatures.
The stable resistance property of manganin ensures that the shunt provides accurate readings over time, making it ideal for long-term usage in industrial and commercial applications.
Voltage Drop & Power Dissipation?
Do you wonder how much voltage drop occurs across a DC current shunt and how it affects power dissipation? Let’s explore this in more detail.
Voltage drop and power dissipation are key factors to consider when choosing a DC current shunt.
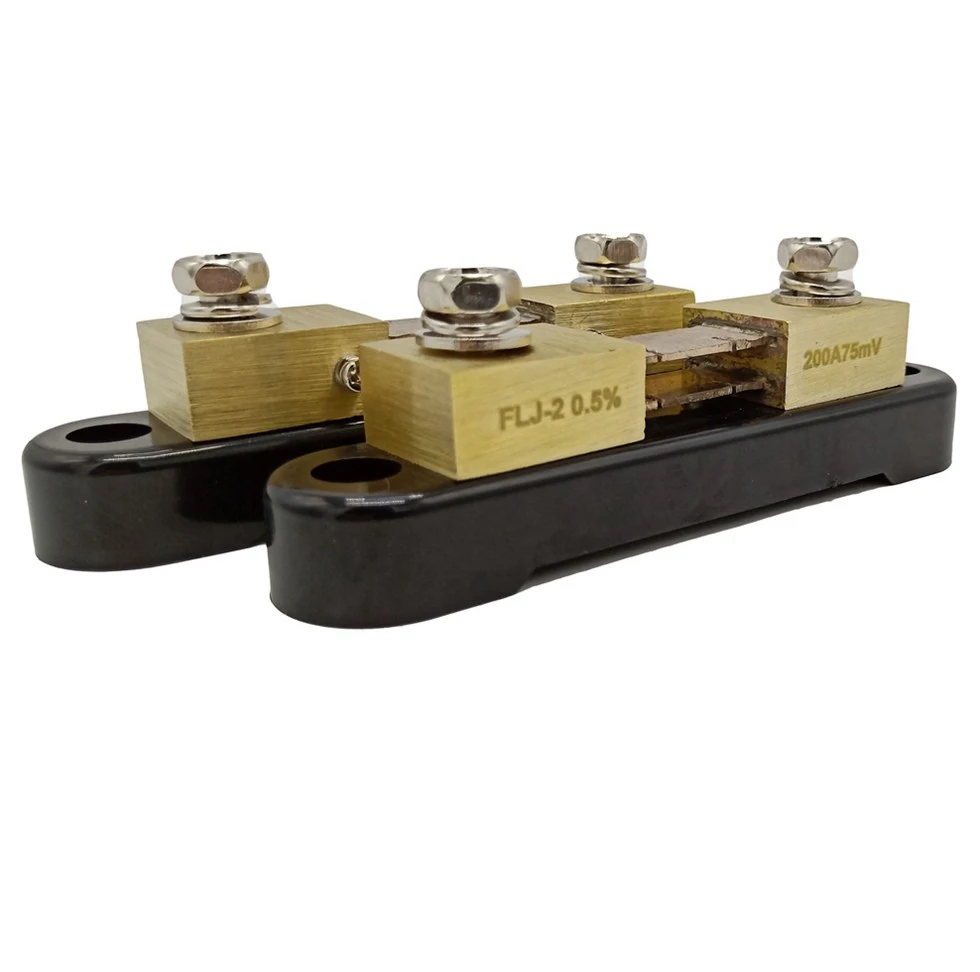

Standard Voltage Drops
When using a DC current shunt, the standard voltage drops are usually:
- 50mV
- 75mV
- 100mV
The choice of voltage drop depends on the application and the range of current that needs to be measured. Lower voltage drops like 50mV are often preferred as they result in lower power dissipation, which helps in reducing heat generation.
Power Considerations
When choosing the right shunt, it’s important to consider the power dissipation. A 50mV shunt is preferred in many applications because it generates less heat, ensuring the system remains efficient without overheating. Excessive power dissipation can lead to overheating, which can affect the shunt’s accuracy and longevity.
For high-current applications, choosing a shunt with a proper voltage drop is essential for balancing between measurement accuracy and power efficiency.
Installation Guidelines?
Wondering how to properly install DC current shunts? Let’s go over the key installation tips.
Proper installation ensures the accuracy and longevity of the DC current shunt, preventing errors in current measurement.
Mounting
- Large Shunts: For high current applications, large shunts should be directly mounted to the bus bar to ensure a secure and stable connection.
- Smaller Shunts: These are typically mounted on an insulating base for panel or enclosure installation, allowing for easier access and maintenance.
Thermal Considerations
Temperature plays a critical role in the performance of DC current shunts. It’s important to ensure that the central operating temperature stays below 80°C. If the temperature exceeds 140°C, the resistance of the manganin alloy may change permanently, leading to inaccurate measurements.
Cooling Requirements
Proper cooling is crucial to prevent overheating. Vertical mounting can support natural convection cooling, allowing the heat to dissipate efficiently. In enclosed spaces, forced air cooling might be required to maintain temperature control and keep the shunt in optimal working condition.
By following these installation guidelines, you can ensure that your DC current shunt operates at peak performance for years.
Electrical Connections & Meter Compatibility?
Are you concerned about the proper electrical connections and which meters are compatible with DC current shunts? Let’s take a look.
For accurate current measurement, it’s essential to maintain proper electrical connections and pair the shunt with the right meter.
Connection Considerations
To avoid errors in current measurement, it’s essential to maintain proper lead resistance. This is because even small changes in resistance can affect the voltage drop and result in inaccurate readings. Ensuring minimal lead resistance helps preserve the accuracy of your measurements.
Meter Pairing
- Digital Meters: Digital meters with high input resistance (1MΩ+) are ideal for pairing with DC current shunts, as they have a negligible impact on accuracy.
- Analog Meters: When using analog meters, the lead resistance must be carefully accounted for, as it can cause significant measurement errors.
Choosing the right meter and ensuring proper electrical connections will help you get the most accurate results from your DC current shunt.
Summary & Best Practices?
Wondering how to ensure your DC current shunt works flawlessly for years to come? Let’s summarize the best practices.
Proper selection, installation, and maintenance of DC current shunts are essential for ensuring long-term measurement accuracy and reliability.
Best Practices
- Choose the Right Shunt: Select a shunt based on the current range and voltage drop requirements for your application.
- Install Properly: Follow proper installation procedures, considering mounting, cooling, and thermal conditions.
- Maintain Electrical Connections: Ensure low lead resistance and use high-quality measuring devices to ensure accuracy.
- Monitor Temperature: Regularly monitor the temperature to prevent overheating and ensure accurate readings.
By following these best practices, you can ensure that your DC current shunt provides reliable measurements over time, contributing to the efficiency of your electrical systems.
Conclusion
In conclusion, DC current shunts are indispensable for accurate current measurement in various electrical systems. Proper installation and maintenance ensure optimal performance.
FAQ
Q: What is a DC current shunt?
A: A DC current shunt is a precision resistor used to measure current by creating a small, measurable voltage drop.
Q: How do I install a DC current shunt?
A: Install the shunt in series with the load, ensure proper electrical connections, and maintain temperature and cooling requirements for optimal performance.
Q: What materials are used to make DC current shunts?
A: DC current shunts are typically made from manganin alloy, which offers low resistance and stability under varying temperatures.
Q: Can DC current shunts be used in AC circuits?
A: No, DC current shunts are specifically designed for DC circuits and are not suitable for AC applications.
Q: How can I ensure the accuracy of my DC current shunt?
A: Ensure proper electrical connections, minimize lead resistance, and pair the shunt with a compatible measuring device. Regularly monitor the temperature to prevent overheating.